Reflow Soldering Technology in PCBA Electronics Assembly
Reflow soldering is the dominant method for attaching Surface Mount Technology (SMT) components to a Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA). It is a highly controlled thermal process designed to melt solder paste, allowing the molten solder to wet the component leads and PCB pads, forming a reliable electrical and mechanical bond upon cooling.
The Solder Paste: The Foundation of the Joint
The process begins with the precise application of solder paste onto the component pads of the PCB. Solder paste is a homogenous mixture of fine metallic solder powder (typically a lead-free alloy like SAC305: 96.5% Tin, 3% Silver, 0.5% Copper) suspended in a sticky, viscous flux medium.
Application: Solder paste is applied using a stencil printing process. A stainless-steel stencil, chemically etched with apertures matching the component pads, is aligned with the PCB. A squeegee blade then pushes the paste through the apertures onto the board.
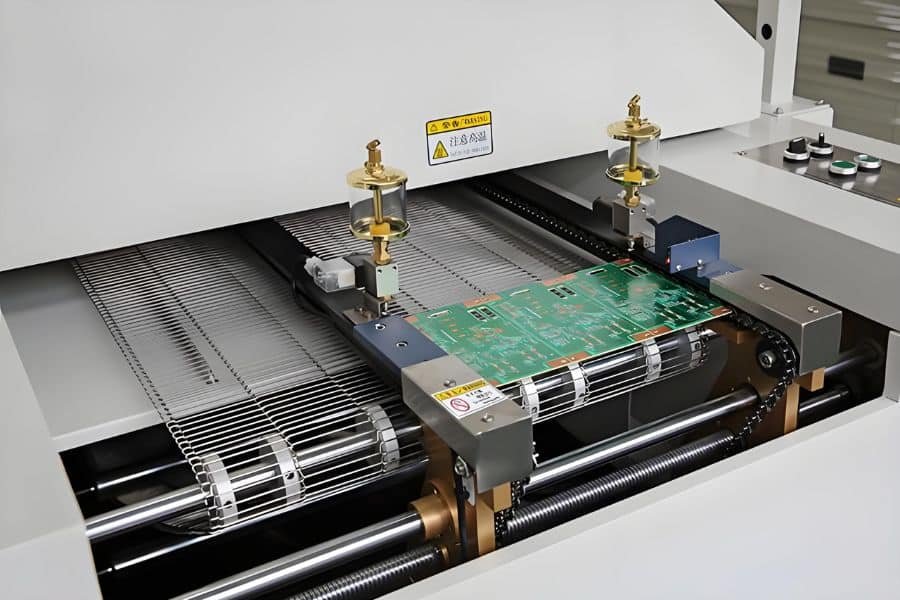
Component Placement: After printing, high-speed Pick-and-Place machines accurately position the SMT components onto the tacky solder paste deposits. The tackiness of the flux holds the components in place prior to reflow.
The Thermal Reflow Profile: A Controlled Journey
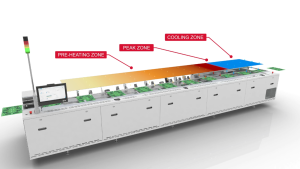
The core of reflow soldering occurs as the assembled PCB travels through a multi-zone reflow oven, which uses forced hot air convection or infrared (IR) heating. The entire process is dictated by a precisely engineered thermal profile, which has four critical stages:
1. Preheating/Ramp-up Zone
Goal: To raise the temperature of the PCB and components at a controlled, uniform rate (typically 1.0 to 3.0 °C/second).
Importance: This minimizes thermal shock to sensitive components, which could cause cracking or damage.
2. Soak/Pre-reflow Zone
Goal: To hold the board at a stable, elevated temperature (often between 150 and 200 °C) for a specific duration.
Importance: This allows the flux to become fully activated, cleaning oxides from the component leads and pads, a process called flux activation. Crucially, it allows all areas of the PCB, particularly large components and dense areas, to reach a uniform temperature.
3. Reflow Zone (Time Above Liquidus – TAL)
Goal: To rapidly increase the temperature above the liquidus temperature (TL) of the solder alloy. For SAC305, TL is 217 °C. The peak temperature is typically 235 to 245 °C.
Importance: The solder powder melts and flows, driven by surface tension to wet the metal surfaces and pull the component into precise alignment (self-alignment). The time spent above TL (TAL) must be minimized to prevent excessive intermetallic compound (IMC) growth, which can embrittle the joint.
4. Cooling Zone
Goal: To rapidly cool the solder joints to below the solidus temperature (TS), typically at a rate of 2 to 5 °C/second.
Importance: Fast cooling ensures a fine, strong metallurgical grain structure in the solder joint. Slow cooling can lead to a coarse, weaker grain structure and poor joint reliability.
Key Advantages and Challenges
Primary Use High-volume SMT assembly and fine pitch components.
Defect Control Excellent control over shorts/bridges due to self-alignment.
Throughput High, as entire panels are processed in one pass.
Challenge Ensuring a uniform thermal profile across large, high-mass boards.
The precise control over the thermal profile is paramount. Deviations can lead to defects like tombstoning (a small component standing on one end), voids (gas bubbles within the joint), and Head-in-Pillow (HIP) defects, making profile optimization a vital part of electronics manufacturing quality control.
P&C Enterprise Solutions (PCES) is a trusted OEM/ODM electronics manufacturer based in Vietnam. Our electronic components and embedded solutions have been delivered to customers across Europe, Asia, and the Middle East, supporting a wide range of industries including audio systems, GPS devices, elevators, lighting, and automation. With strong in-house capabilities in product design, hardware, firmware, and mass production, we provide fully customized solutions tailored to your specific project requirements.
PCES